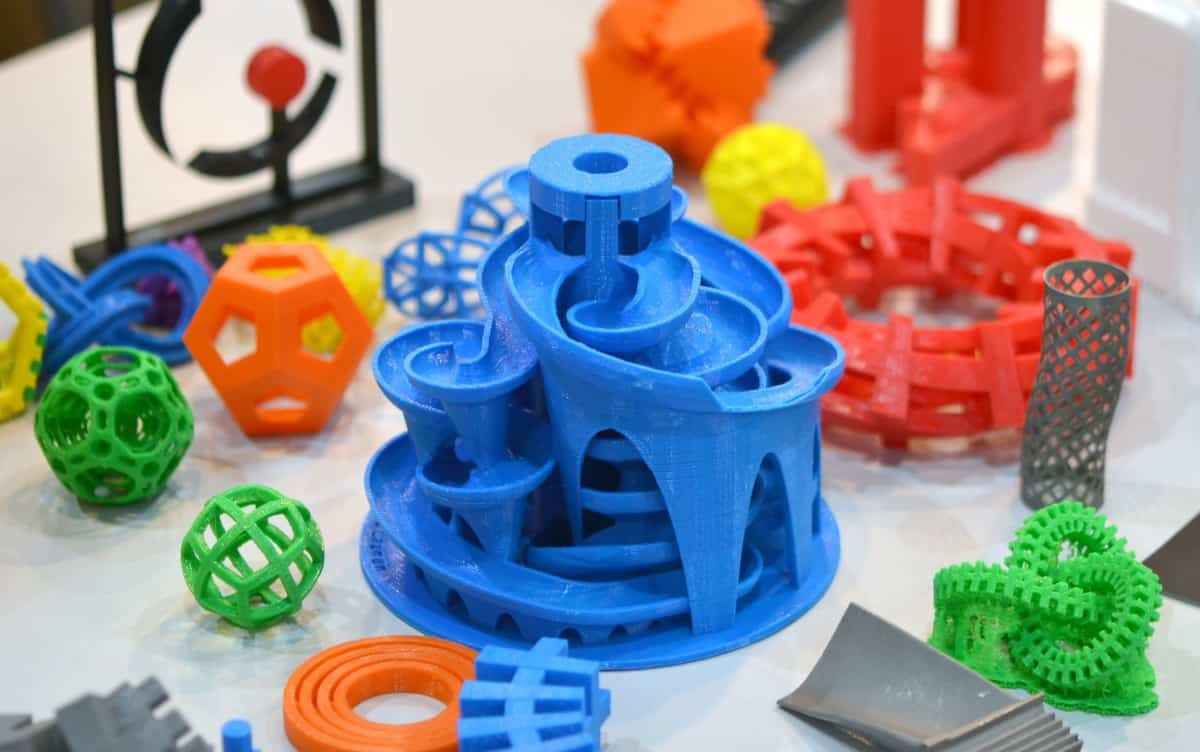
3D Printing technology has taken the world be storm and I too had to get my hands on one. 3D printing can be fun and exciting as it allows designer to 3d print their CAD models with ease, the opportunity and freedom never before available. But owning a 3d printer is not so exciting if you can not get perfect prints out of it and in this article I will show you exactly how to calibrate your 3d printer to get desired perfect 3d prints that look great and dimensionally accurate.
To achieve desired results with 3d printer for perfect quality of good looks and dimensionally accurate 3d printed models it is important to know that 3d printer is properly calibrated. Here I will show you how to calibrate your 3d printer step by step in order to get the best results out of every print.
Table of Contents
Calibrating Extruder E-steps

The first thing you would want to do before anything is to check the calibration of the extruder E-steps.
E–steps in 3d printer are the number of steps the extruder stepper motor needs to make to extrude one millimeter of filament. Poor calibration of the extruder esteps will end up with some very unpleasant over or under extrusion results.
Calibrating Extruder esteps is not difficult and easy to check by simply measuring and marking 100mm on the filament at the extruder stepper motor, then tell the printer to extrude 100mm and see if it stops at the 100mm mark on the filament.
By default most 3d printers come tuned it pretty close but if for any reason you find that your printer is over extruding or under extruding you can find instruction with pictures in my other post here: on How to calibrate extruder E-steps. Be sure to check it out.
Next step is to calibrate the flow of filament.
Calibrating Flow and setting extrusion multiplier
Do not let the calibration of flow and esteps confuse you as they are not the same thing. Now that you have your esteps calibration completed and your 3d printer knows to dispense precisely 100mm of filament when 100mm of filament is needed.
Next, you want to be sure that your 3d printed model will be dimensionally correct by calibrating flow of material by adjusting the extrusion multiplier in the slicer setting. This is very important as the flow may very slightly when between types of materials, brands, and even colors within a brand of filament.
The good news is you may only need to do this once per filament and then you can save your settings in a slicer profile for future use.
How do I calibrate flow on my 3d printer to get dimensionally accurate models?
One of the most important things for good quality and dimensionally accurate 3d prints is to get the flowrate / extrusion multiplier correct for your type of filament. Good news is that it’s easy to dial in.
First, make sure your extrusion multiplier is set to 1 in your slicer.

How-To calibrate flowrate for, 0.40 mm nozzle
Download my flow calibration cube in the download page above or you can find one on thingiverse.

When using a 0.40 mm nozzle, set the line width to exactly 0.40 mm in your slicer and print calibration cube which has 0.80 mm walls. After you have printed it, measure the thickness of all four walls with a caliper and take a note of the widths. Let’s say these are the widths of the walls measured:
Wall 1 = 0.81,
Wall 2 = 0.82,
Wall 3 =0.83,
Wall 4 = 0.83
Then the formula to calculate the flow rate is:
0.80 / ((0.81 + 0.82 + 0.83 + 0.83) / 4) ≈ 0.97
or simply add all 4 walls values which equals to 3.3 and divide by 4 walls to get 0.825 average flow.
Then, take the expected 0.80 flow and divide by actual flow 0.825 that equals to 0.969. This is a new value for extrusion multiplier. Since the actual flow rate is more than expected, we will need to reduce the multiplier in slicer by 3% in our example.
So, the flowrate or extrusion multiplier is about 97% or 0.97 which you then set in your slicer. Print the cube again to confirm. The measured walls should now be very close to 0.80 mm thick.
Be sure to hit update profile button to save your slicer profile settings.

Repeat this process as many times as necessary until desired results are achieved.


Calibrating Temperature for 3D Printing Filament. | Printing Tower
Now would be a good time to 3d print a temperature calibration tower to further perfect your 3d printing experience. This tower can be found on thingiverse as well as in the download page above.
The advantage of 3d printing a temperature tower is that it will clearly show you the best results at a specific temperature for that particular filament that you are using.
Printing a temperature tower is something that I do with every new type of filament including different color filament from the same brand.
3D printed temperature tower like the one pictured in the example will provide you with a preview of the results not only for temperature levels but also bridging, overhang, and some stringing.
After 3d printed tower is completed and the desired temperature level is determent. Take note of that temperature for that specific Brand, type, and color of filament.
How To Stop Stringing and Blobbing | 3D Printer Calibration
Stringing and blobbing is one of the most common and frustrating issues every 3d printing enthusiast experience, especially when 3d printing with PETG, ABS, and the famous TPU.
Main cause of stringing and blobbing with 3d printing is the elastic properties of the filament. However both stringing and blobbing can be greatly reduced or eliminated with proper slicer profile settings and calibration. Below I will walk you step by step on how to make your 3d printer stop stringing.



How to stop stringing on 3d printer | Examples and illustrations
First step to take is to download my string calibration model from our download tab above or find one similar on thingiverse. Then make a copy of a slicer profile that you will be modifying and save a backup copy to fall back on just in case something doesn’t go as planned.
Illustrations below will be in Simplify3d slicer although the setting will be very similar in all other slicer software and the settings I use in the examples are for my PETG filament.
Here are some of the factors that play a major role in stringing filament when 3d printing.
- Hot end nozzle temperature too high.
- Moisture in the filament.
- Retraction distance of filament before nozzle movement thru open space.
- Retraction vertical lift or Z-Hop.
- Speed of filament retraction and nozzle movement when not printing.
- Nozzle coasting and wipe distance.
Hopefully at this point you already know your desired temperature setting for your filament, which alone will reduce much of stringing and to completely master it slicer software gifted us with an “ooze control” settings that we can fine tune for our specific 3d printer and filament.


Retraction setting is one of the most important setting that you will use for string control. What retraction does is it actually pulls the filament back into the nozzle at the end of each print line before moving to next point and this relieves pressure built in the nozzle that would ultimately continue to come out of the nozzle in the unintended space.
Retraction distance setting is also very sensitive to the type of filament you may be 3d printing. This may be more forgiving to the common PLA rather than flexible filaments like TPU.
Most filament will absorb moisture from the air and some may do so much quicker than other. Moisture in the filament is one of the most common reason for stringing in 3d prints. Best solution to this is to make sure the filament is completely dry before 3d printing, and for that I use filament dryer I bought on Amazon.
Check out the link to see the latest price for the filament dryer on Amazon.